Updated on March 25, 2025
Usage Statistics and Success Rates of Different Contact Lenses


Vision Center is funded by our readers. We may earn commissions if you purchase something via one of our links.
Around 45 million people in the United States rely on contact lenses for vision correction, reflecting a consistently high demand for options that balance comfort, safety, and cost. While soft lenses remain the predominant choice, more specialized lens types have steadily grown in both availability and popularity over the past five years.
Broadly speaking, contact lens modalities can be categorized into soft lenses (daily disposable, biweekly, monthly), rigid gas permeable (RGP) lenses, hybrids, and sclerals.
Each category features its own unique advantages and drawbacks, ranging from initial comfort and convenience to visual acuity and long-term safety outcomes. The data gathered here reflects shifts in prescribing habits, cost analysis, and real-world patient experiences, aiming to provide a clear overview of how and why individuals and practitioners choose different contact lens types.
Key Statistics at a Glance
- High Market Share of Soft Lenses: Soft lenses account for an estimated 84% to 90% of wearers in the United States.
- Rapid Growth in Daily Disposables: Daily disposable soft lenses now represent 35% to 40% of all U.S. soft lens wearers and up to 60% of total lens sales by value.
- Rigid Lenses as a Niche: RGP lenses are used by only 7% to 11% of wearers, but they remain vital for achieving sharp optics, particularly for those with high astigmatism or corneal irregularities.
- Cost Differences: Annual expenses can vary widely by lens type. Daily disposables typically cost $600 to $900 annually, while monthly lenses, including care solutions, can run $300 to $450 per year.
Contact Lens Prevalence and Trends
Understanding the distribution of different lens types is critical for appreciating how technological advancements and patient needs shape the broader market.
Recent data suggests that patient preference for convenience, eye health, and improved designs has driven significant growth in daily disposable soft lenses. Meanwhile, specialty lens categories, such as sclerals and hybrids, offer targeted solutions for complex prescriptions or medically necessary situations.
- Soft Lenses Dominance:
- Roughly 84% to 90% of U.S. contact lens wearers use soft lenses.
- Daily disposable soft lenses have seen a strong uptick in prescriptions, moving from around 38% of new soft fits in 2019 to a 35% to 40% share among total wearers by 2023.
- Toric soft lenses (for astigmatism) and multifocal soft lenses (for presbyopia) also show consistent expansion, now capturing roughly 25% and 10% of the soft lens market (by revenue), respectively.
- Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) and Specialty Lenses:
- RGP lenses currently represent about 7% to 11% of the contact lens market, favored for their high optical clarity and durability.
- Scleral lenses (a subset of RGPs) have grown to 4% to 7% of all fits, primarily due to their comfort and success in irregular cornea cases.
- Hybrid lenses remain less than 1% of total lens usage but can be invaluable for patients who want RGP-level vision with softer edges.
- Extended-Wear Decline:
- While extended-wear lenses exist for continuous overnight use, only about 5% of soft lens fits in the U.S. are designated for extended wear, reflecting concerns about increased infection risk.
Success Rates and Comfort
A lens’s success depends on comfort, clarity, and long-term tolerability. Advances in material science, particularly silicone hydrogel technologies, have elevated oxygen permeability and overall comfort. However, the required adjustment period, care regimen, and specific patient needs still vary significantly among lens types.
- Soft Lenses:
- Often show an immediate comfort advantage.
- Comprise ~90% of wearers, yet about 21.7% eventually discontinue, typically citing dryness or unsatisfactory vision.
- Patient “refits” are successful in roughly 75% of dropout cases, highlighting that targeted solutions (e.g., different lens materials or daily disposables) often resolve comfort issues.
- Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) Lenses:
- Require a 10 to 15 day adaptation period. Approximately 27% of new RGP wearers drop out before the two-week mark due to initial discomfort.
- Long-term wearers who adapt often report excellent vision and high satisfaction, with about 70% success rates in routine corrections and closer to 90% for therapeutic or complex cases.
- Scleral Lenses:
- Designed to vault the cornea entirely, resting on the sclera.
- Provide exceptional comfort and stability for patients with keratoconus, severe dry eye, or other corneal irregularities; around 78% to 88% report substantial improvement in comfort and vision.
- Handling remains a challenge, with more involved insertion and lens filling steps.
- Daily vs. Extended Wear:
- Daily disposable lenses now rank among the safest and most comfortable options, as each use starts with a fresh sterile lens.
- Extended-wear lenses appeal to a small subset of users requiring the convenience of overnight wear but carry roughly tenfold higher infection rates than daily wear.
Patient Experience and Satisfaction
Beyond raw clinical performance, patients evaluate their contact lenses in terms of day-to-day convenience, adaptability, and overall quality of life improvements.
- Adaptation Period:
- Soft lenses have minimal adaptation time; most new wearers adjust within days.
- RGPs demand patience during the initial weeks, but once adapted, comfort scores are often on par with soft lenses.
- Scleral lenses are relatively comfortable from the start due to minimal corneal contact but require specialized insertion training.
- Compliance and Maintenance:
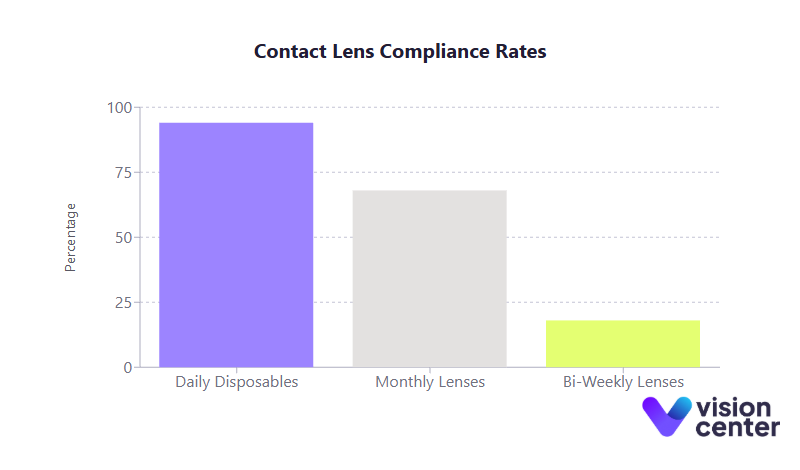
- Daily disposables show the highest compliance rates (around 94%), mainly because they eliminate nightly cleaning.
- Monthly and biweekly lens wearers must adhere to proper cleaning protocols; only 68% of monthly lens users and 18% of two-week lens users meet ideal compliance guidelines.
- Noncompliance (e.g., topping off solution, sleeping in non-approved lenses) significantly raises the risk of serious eye complications.
- Quality of Life:
- Approximately 8 in 10 contact lens wearers prefer them over glasses for daily activities and self-perception.
- Children and teenagers often report improved self-esteem when switching from glasses to contacts, while adults emphasize the benefits during sports and physical activities.
- Specialty lens wearers (e.g., scleral wearers with severe dry eye) frequently describe their lenses as “life-changing,” allowing longer wear times and normal work or leisure routines.
Clinical Outcomes and Safety
Though contact lenses are generally safe, they do carry a non-negligible risk of complications, particularly if wear and care guidelines are ignored.
- Infection Risk:
- Daily-wear soft lenses see 2 to 4 cases of microbial keratitis per 10,000 users annually, whereas extended-wear soft lenses can reach 20 cases per 10,000.
- Daily disposable modalities present the lowest infection rates across soft lens categories.
- An estimated 1 million Americans experience some form of lens-related eye infection or inflammation each year, though most resolve without lasting vision loss.
- Complications and Discontinuation:
- Common issues include corneal hypoxia (if oxygen transmission is insufficient), dry eye, deposit buildup, and giant papillary conjunctivitis (in response to protein deposits).
- About 16% of serious keratitis cases can result in permanent vision impairment, though strict compliance markedly reduces this risk.
- Discomfort and dryness remain the top reasons for patient dropout, but proper refitting and lens type adjustments often restore successful wear.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
A comprehensive view of contact lenses must consider both their performance and associated financial impacts. Annual costs differ greatly by lens type, factoring in supplies, replacement frequency, and professional fitting services.
| Lens Modality | Replacement Frequency | Approx. Annual Lens Cost | Approx. Solution Cost | Total Annual Estimate | Key Points |
| Daily Disposable (Soft) | New pair each day | $600 to $900 | $0 | $600 to $900 | Highest convenience and safety; costlier for daily wear. |
| Monthly Disposable (Soft) | Once per month | $180 to $300 | $100 to $150 | $300 to $450 | More economical for full-time wear; moderate cleaning effort. |
| Biweekly Disposable (Soft) | Every two weeks | $270 to $360 | $100 to $150 | $390 to $480 | Similar to monthly but replaced more frequently. |
| Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) | 1 to 2+ years | $100 to $200/year (averaged) | $100+ | $200 to $300 | Lower long-term costs but higher upfront fitting fees. |
| Scleral/Hybrid (RGP) | ~Annually (custom) | $500 to $1200+ | $200+ | $700 to $1400+ | Essential for complex cases; higher overall expense. |
- Daily vs. Monthly Cost-Effectiveness:
- Full-time daily disposables generally cost more per year than monthly lenses.
- Part-time wearers (e.g., a few days per week) may find dailies cost-effective, as they pay only for the days they use lenses and avoid solution expenses.
- RGP Durability Advantage:
- RGPs can be replaced once every year or two, making them potentially cheaper in the long run.
- Success hinges on adapting to their steeper early comfort curve and handling routine.
- Specialty Lenses:
- High upfront costs for scleral or hybrid fits often include multiple visits and custom lens fabrication.
- Insurance may cover a portion if the lenses are medically necessary (e.g., keratoconus or post-surgical corneas).
Many practitioners balance cost considerations with health outcomes, often recommending daily disposables for improved safety and compliance if the budget allows.
Patients who require advanced optical correction or long-term durability may still find RGPs or specialty lenses more viable. Ultimately, a thorough professional evaluation helps pinpoint the lens type that best fits each individual’s visual needs, lifestyle, and financial realities.
Final Summary
In daily practice, eye care professionals advise that proper compliance, regardless of lens type, can drastically reduce overall costs by minimizing infection treatments and additional medical visits. For some, daily disposables present an obvious advantage in convenience and lower complication rates. Others, especially those wearing lenses constantly, may prefer monthly reusables or RGPs to save money over time.
Over the past five years, emerging materials and designs have expanded contact lens accessibility, leading to a noticeable shift toward healthier, more convenient daily disposables, without entirely displacing the budget-friendly or specialty-oriented options. Success rates remain high across soft and rigid categories as knowledge of proper lens care grows, and more patients discover advanced fits for unique ocular needs.
Looking ahead, these data-driven insights suggest that technological improvements will continue to shape practitioner recommendations. Additionally, steady consumer demand for convenience and eye health should further drive the adoption of daily disposables, especially as production scales up and costs potentially moderate.
In the end, the sheer variety in lens options ensures most people can find a comfortable, safe, and cost-appropriate solution. By merging patient education with ongoing improvements in lens materials and design, the field continues to advance, supporting millions of contact lens wearers in clearer, healthier vision for years to come.
16 sources cited
Updated on March 25, 2025
Updated on March 25, 2025
About Our Contributors
Mara Sugue, with a B.A. in Social Sciences, is a dedicated web content writer for Vision Center. She is committed to making eye health research accessible and understandable to people from diverse backgrounds and educational levels. Her writing aims to bridge the gap between complex vision health topics and readers' needs for clear, factual information.
Dr. Melody Huang is an optometrist and freelance health writer with a passion for educating people about eye health. With her unique blend of clinical expertise and writing skills, Dr. Huang seeks to guide individuals towards healthier and happier lives. Her interests extend to Eastern medicine and integrative healthcare approaches. Outside of work, she enjoys exploring new skincare products, experimenting with food recipes, and spending time with her adopted cats.

