Updated on March 21, 2025
What Are Some Trends in Contact Lens Usage?


Vision Center is funded by our readers. We may earn commissions if you purchase something via one of our links.
Contact lenses have become an integral part of vision correction for millions of people. They offer unique advantages over traditional eyeglasses, including a broader field of view, greater convenience for sports and activities, and cosmetic appeal.
In this article, we explore the most up-to-date statistics on contact lens usage, complications, market influence, and long-term outcomes.
By examining recent data, we aim to shed light on how contact lens wear has evolved over the past five years, who is most likely to wear them, and what factors influence their safe use and affordability.
Broader Overview of the Topic
Contact lenses are considered medical devices in the United States and require a valid prescription. Over time, significant technological advances, such as silicone hydrogel materials and daily disposable designs, have helped improve comfort, reduce risks, and expand contact lens use to more populations, including younger children for myopia management.
Yet, challenges remain. Non-adherence to recommended lens care regimens, overnight wear, and exposure to tap water or other sources of contamination can lead to eye infections and other complications.
At the same time, the contact lens market continues to grow, with new products introduced every year and major manufacturers vying for a share of an industry worth billions of dollars.
Key Contact Lens Statistics
- Around 45 million Americans currently wear contact lenses, representing roughly 16% of U.S. adults.
- Soft disposable lenses dominate the U.S. market at about 93% of overall contact lens fits.
- About 50% of wearers acknowledge sleeping in their lenses at least occasionally, a practice that increases infection risk by up to 10×.
- The U.S. contact lens market was valued at approximately $10.94 billion in 2022, illustrating the sizable economic footprint of this vision-correction modality.
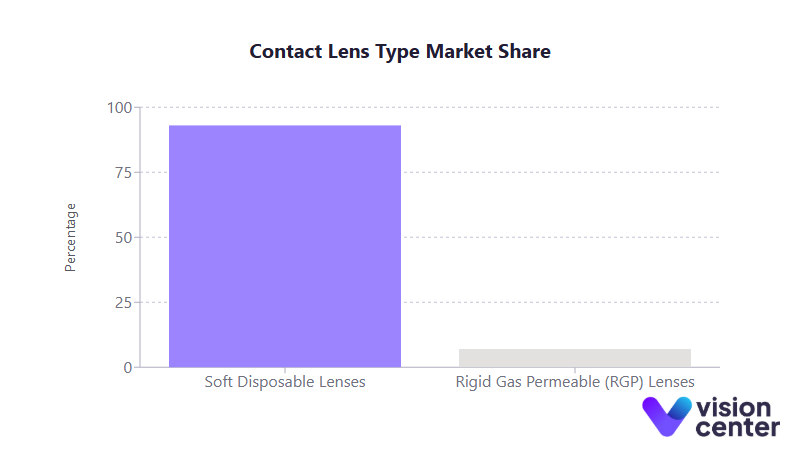
Prevalence and Demographic Breakdown
Understanding who wears contact lenses and why is foundational to grasping larger trends in eye care. Demographic data reveals differences in age, gender, and lens preferences that shape the overall market.
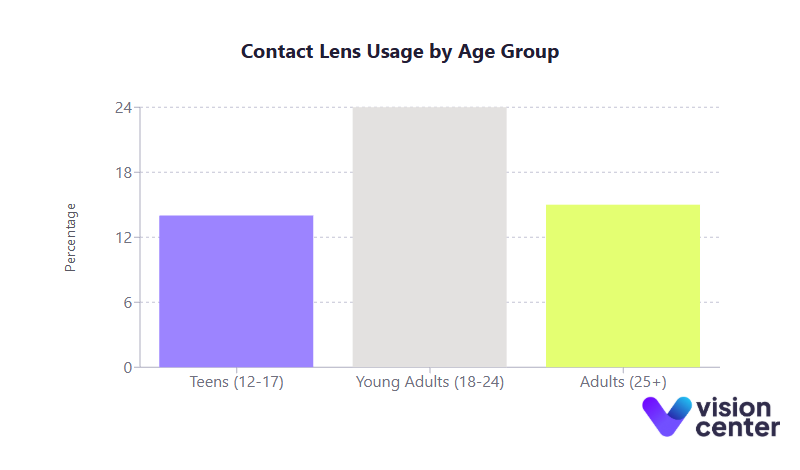
Age Group Distribution
- Teenagers (12 to 17 years): Around 14 to15% of teens wear contact lenses. Many in this age group choose contacts for sports or cosmetic reasons, though compliance can be challenging.
- Young Adults (18 to 24 years): Approximately 24% wear contacts, the highest percentage among all age groups. They typically prefer the convenience and aesthetics that contact lenses provide compared to glasses.
- Adults (25+ years): An estimated 15% continue wearing lenses past age 25. Usage declines further in middle age and beyond, largely due to presbyopia, ocular dryness, or comfort issues.
By gender, roughly two-thirds of U.S. contact lens wearers are female. Studies suggest that both the higher prevalence of refractive errors among women and cosmetic preferences contribute to this disparity.
Total Wearers: Across all ages, approximately 45 million Americans wear contact lenses. This marks a steady increase from earlier in the decade, reflecting advancements in lens comfort and broader acceptance of contact lens use.
Lens Type Preferences
- Soft Disposable Lenses: Represent about 93% of all contact lens use in the United States, with daily disposables accounting for a rapidly growing segment, now nearly half of new soft lens fittings.
- Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) Lenses: Comprise roughly 7% of users. Within RGPs, specialized designs like scleral lenses (for keratoconus or severe dry eye) and orthokeratology (overnight corneal reshaping) are growing in niche popularity but still represent a small fraction of overall fits.
The shift toward disposable soft lenses aligns with convenience and safety benefits. RGPs remain an important option for patients with irregular corneas or high astigmatism and are sometimes more durable, but they require specialized fitting and consistent wear time for adaptation.
Trends Over Time
Increased Popularity of Daily Disposables
One of the most significant shifts in recent years is the surge in daily disposable contact lenses. Formerly considered premium-priced, single-use lenses now make up close to half of new soft lens fits. Practitioners note that daily disposables reduce the risk of contamination associated with cleaning and storing lenses, which translates into fewer lens-related eye infections.
Despite the higher annual expense, many wearers find the convenience and enhanced safety worth the cost. Some also report better end-of-day comfort, as each pair of lenses is used only once.
Decline of Extended Wear
Extended-wear lenses, meant to be slept in continuously for up to 30 nights, have fallen sharply in popularity. Although certain silicone hydrogel materials offer high oxygen permeability, overnight lens use significantly increases the risk of microbial keratitis (corneal infection).
Consequently, the majority of U.S. eye care providers now recommend daily removal, even if the lens is approved for extended wear.
Specialty Fits and Myopia Management
In addition to mainstream soft lenses, eye care practitioners are embracing specialized designs:
- Scleral Lenses: Used increasingly for conditions like keratoconus, severe dry eye, and post-surgical corneas.
- Multifocal and Toric Soft Lenses: Address the needs of presbyopes and those with higher levels of astigmatism.
- Orthokeratology and Myopia Control Lenses: Rapidly adopted to slow myopia progression in children and adolescents. Pediatric fits are on the rise, reflecting a major new direction in contact lens prescribing.
Key Influencing Factors: Health and Safety
Contact lenses are generally safe when used properly, but complications can occur. Both the lens type and wearer behavior play crucial roles in determining safety outcomes.
Complication Rates by Lens Type
- Microbial Keratitis: A serious corneal infection, with incidence ranging from about 2 cases per 10,000 wearers (RGP daily wear) up to 20 per 10,000 for those sleeping in soft lenses. This demonstrates how overnight lens use can be 5 to 10 times riskier than daily-wear routines.
- Corneal Inflammation and Ulcers: Extended-wear lenses carry higher risks of sterile ulcers and inflammatory events. Modern materials have reduced hypoxia-related issues, but overwear remains a primary risk factor.
- Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis (GPC): Protein deposits on lenses can trigger chronic inflammation on the inner eyelid. The frequent replacement cycles of today’s lenses have lowered GPC rates, though it still appears in some long-term wearers.
- Dry Eye and Discomfort: About 55% of wearers report intermittent dryness. End-of-day discomfort is a leading cause of decreased wearing time and an important contributor to dropout rates.
Each year, an estimated one million health care visits in the U.S. involve contact lens-related keratitis or complications, with an annual cost of $175 million to the healthcare system. Many of these complications are preventable with proper lens care and regular follow-up exams.
Compliance and Adherence
Poor compliance remains the single biggest catalyst for contact lens problems:
- About 50% of wearers say they sleep or nap in their lenses, at least occasionally.
- Nearly half admit extending lens replacement beyond recommended schedules (e.g., wearing 2-week lenses for 3+ weeks).
- Over 80% keep their lens case longer than recommended, and 55% “top off” solution instead of discarding old solution.
- 84.9% shower with lenses in, and 61% swim in them, exposing lenses to tap or pool water, which can harbor microbes.
These risky behaviors significantly increase rates of eye infections. Although educational campaigns highlight the importance of proper care (no overnight wear, replace lenses on time, never expose lenses to water), the compliance gap persists.
Impact of the Topic: Long-Term Outcomes and Dropout
Long-Term Ocular Health
When properly managed, long-term contact lens wear is compatible with stable ocular health. Modern lens materials have reduced issues like corneal hypoxia. However, chronic non-compliance can lead to:
- Recurrent inflammation or mild corneal changes
- Dry eye syndrome or contact lens-induced papillary conjunctivitis
- Possible corneal neovascularization (though less common with high-oxygen silicone hydrogel materials)
Routine yearly or biannual check-ups are essential to catch and manage these issues early. Most long-term wearers who follow the recommended guidelines maintain excellent vision and comfort for decades.
Dropout Rates and Satisfaction
Dropout often happens within the first year of wear. Some estimates suggest around 25% of new users revert to glasses in that time. Leading causes include:
- Discomfort or dryness
- Unsatisfactory vision with lenses (especially for astigmatism or presbyopia)
- Convenience and cost concerns
However, among those who continue wearing lenses beyond one to two years, the majority rarely discontinue afterward. Published retention studies and long-term surveys generally show high satisfaction among established wearers. This underscores that while early dropout can be significant, established wearers typically remain dedicated to contact lens use.
Financial and Social Consequences
Cost Analysis
From a consumer standpoint, contact lenses can represent a substantial ongoing expense. Total annual cost varies widely based on lens type, replacement schedule, solutions, and whether the wearer needs specialty lenses such as toric, multifocal, RGP, or scleral designs.
Professional services add to the bill. Most contact lens wearers pay extra for a contact lens fitting/evaluation on top of a routine exam. Those lacking vision insurance may be more inclined to stretch the life of their lenses or skip routine check-ups, increasing the risk of complications.
On the healthcare system side, complications drive $175 million in direct costs annually. Reducing infection rates through better education and improved lens technology could mitigate these avoidable expenses.
Manufacturer Landscape
The U.S. contact lens market remains concentrated among a small group of major manufacturers, and industry reports continue to show strong competition around daily disposables, toric lenses, multifocals, and specialty fits.
That concentration shapes product innovation, practitioner education, and the pace at which new materials and replacement modalities reach patients.
Insurance Coverage and Accessibility
Vision insurance can significantly improve affordability for contact lens wearers by offsetting annual exams, fitting fees, and part of the lens cost. Coverage requirements also encourage regular exams and prescription renewal, which can indirectly support safer wear habits.
In contrast, individuals without insurance or with minimal coverage may buy lenses online in smaller batches or extend wear schedules, raising the risk of lens-related problems. Thus, insurance availability and coverage policies remain influential in both adoption rates and overall public health outcomes.
Patient Outcomes and Provider Trends
Satisfaction Rates
Established contact lens wearers generally report high satisfaction. The main reported benefits include:
- Improved appearance and self-confidence
- Freedom from eyeglasses for sports and daily activities
- Superior vision quality compared to glasses (especially for high prescriptions or anisometropia)
While comfort has historically been a challenge, modern silicone hydrogel materials and improved designs have reduced dryness and irritation. Still, some users experience end-of-day dryness or night-vision difficulties (halos, glare). These remain the top areas for product innovation.
Healthcare Provider Prescribing Patterns
Eye care professionals have adjusted their recommendations to balance safety, convenience, and patient preference:
- Daily Disposables First: Many optometrists now prescribe single-use lenses as the default choice for new wearers or those who struggle with compliance.
- Reduced Emphasis on Extended Wear: Overnight lens use is discouraged except in limited circumstances due to an elevated infection risk.
- Specialty Lenses for Complex Needs: Providers increasingly fit scleral lenses, custom RGPs, or toric/multifocal soft lenses to serve patients with irregular corneas or presbyopia.
- Myopia Control in Children: Orthokeratology and specially designed multifocal soft lenses are gaining momentum for slowing myopia progression.
- Compliance Education: Many practices focus on patient education, encouraging proper hygiene, regular lens replacement, and routine follow-up exams to reduce complications.
Taken together, these trends suggest that practitioners are moving toward the safest, most user-friendly lens options while also embracing specialty tools for specific clinical needs.
Final Summary
Recent statistics show that contact lenses remain an increasingly popular method of vision correction, with around 45 million Americans relying on them for daily convenience and improved quality of life.
Usage demographics reveal the highest adoption rates among teens and young adults, while adherence challenges persist among wearers of all ages. Non-compliant behaviors, like sleeping in lenses or exposing them to water, amplify infection risks and lead to significant healthcare expenditures. Nevertheless, overall satisfaction levels remain high, and those who adapt well to lenses rarely discontinue.
Looking forward, the contact lens landscape will likely continue evolving through advancements in materials and specialty designs, from myopia control options for children to multifocal lenses for presbyopes.
Strong market competition among a few key manufacturers is driving innovation, although affordability can still be a barrier. With strategic insurance coverage and ongoing education, more wearers may enjoy the benefits of contact lenses safely and comfortably over the long term.
10 sources cited
Updated on March 21, 2025
Updated on March 21, 2025
About Our Contributors
Mara Sugue, with a B.A. in Social Sciences, is a dedicated web content writer for Vision Center. She is committed to making eye health research accessible and understandable to people from diverse backgrounds and educational levels. Her writing aims to bridge the gap between complex vision health topics and readers' needs for clear, factual information.
Dr. Melody Huang is an optometrist and freelance health writer with a passion for educating people about eye health. With her unique blend of clinical expertise and writing skills, Dr. Huang seeks to guide individuals towards healthier and happier lives. Her interests extend to Eastern medicine and integrative healthcare approaches. Outside of work, she enjoys exploring new skincare products, experimenting with food recipes, and spending time with her adopted cats.

