Updated on September 24, 2024
Why Are Grey Eyes So Rare?


Vision Center is funded by our readers. We may earn commissions if you purchase something via one of our links.
Grey eyes are a rare and distinctive eye color. This eye color only occurs in only about 3% of the global population. Their unique appearance often sets individuals with grey eyes apart. But what factors contribute to the presence of grey eyes?
What Causes Grey Eyes? Are They Rare?
Grey eyes, like all eye colors, owe their existence to the levels of melanin in the iris. People with light-colored eyes have very little melanin compared to brown ones.
People with green or hazel eyes have less melanin, while those with blue eyes have even less. And if you have gray eyes, People with gray eyes have none at all.
Those with gray eyes also have more collagen in their stroma (a layer in the iris). It causes light to scatter differently and creates that unique grey hue. But that's just one piece of the puzzle.
There are at least 16 different genes that play a role in determining a person’s eye color, and scientists are still figuring out how they all work together.
The Global Distribution and Rarity of Grey Eyes
Gray eyes are not distributed evenly throughout the world. Less than 3% of the world’s population has them. They’re most common in Europe, especially in Northern and Central European countries like Iceland, Ireland, Sweden, Finland, and Norway.8
In other parts of the world, they’re much less common. For example, in Asia and Africa, grey eyes are rare. In the U.S., you can commonly see them in people of Northern European descent.
With contact lenses, however, anyone can temporarily change the color of their eyes. It makes it difficult to estimate the distribution of grey eyes in the world accurately.
Are People With Grey Eyes More at Risk for Eye Problems?
Like other people with light eyes, gray eyes are more susceptible to ocular melanoma. This eye cancer affects the layer of the eye called the uvea.
Ocular melanoma can lead to complications such as glaucoma, vision loss, and even the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.
Fortunately, this condition is rare, affecting only six out of every million people in the U.S. annually.6 So, while caring for your eyes is essential, living in fear is unnecessary.
What are Some Benefits of Grey Eyes?
People with light-colored eyes, like grey, are perceived as more intelligent, calm, and profound. They’re also less likely to have certain skin diseases or autoimmune disorders.
Grey eyes can also make you even more attractive. According to a 1000-person poll by 1800Contacts, men rated women with grey eyes the most alluring.2
What Grey Eyes Look Like (Pictures)

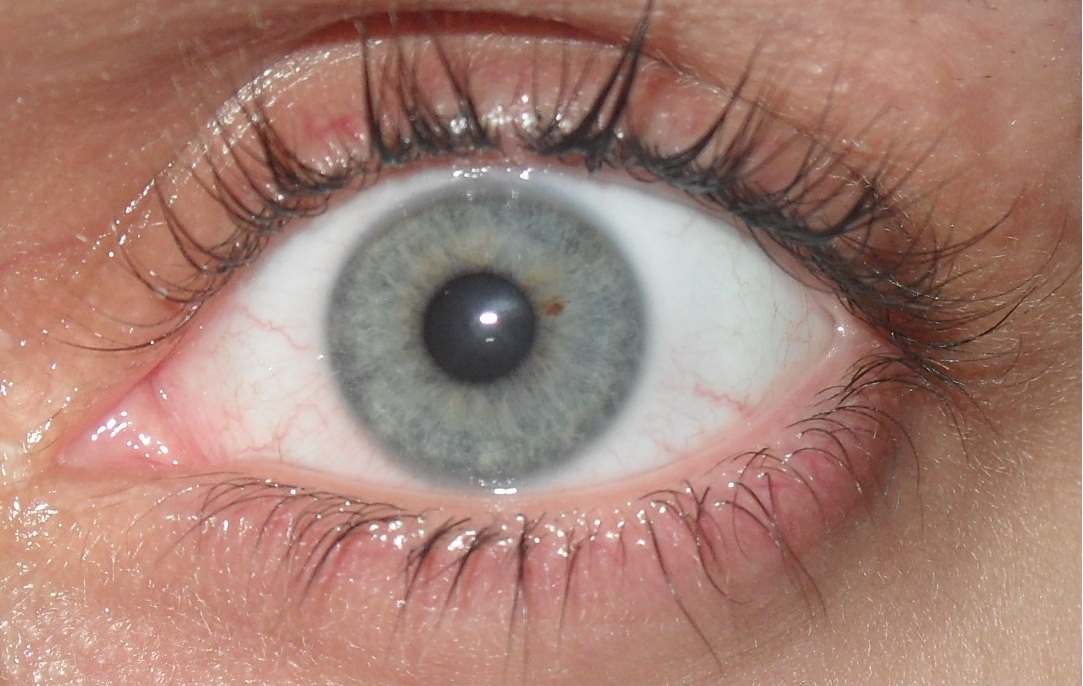
Gray eyes can come in various shades, from light to dark gray. They can even look almost blue. That's why it's easy to mistake them for a blue pair. Gray eyes can also have hints of green or hazel, creating unique and striking variations.
Gray vs. Blue Eyes
A common misconception is that grey eyes resemble light blue eyes, but the two are fundamentally distinct colors.
One way to tell them apart is by looking at the hue. Blue eyes have a cobalt blue or sapphire color. They also tend to be lighter around the edges and darker in the center.
Gray eyes, on the other hand, are usually darker around the edges and lighter in the middle. This unique coloration and its rarity are why so many find grey eyes captivating.
Another reliable way to tell them apart is by looking at the specks within the iris. Blue eyes often have yellow or gold flecks, while grey eyes typically have brown ones.
Furthermore, blue eyes appear brighter and more vibrant, while grey eyes often appear muted or cloudy.
Variations of Grey Eyes
Below are some examples of what gray eyes can look like:
- Grey-green eyes. The iris has a combination of grey and green elements.
- Dark or steel gray eyes. The iris has a deep grey hue and often has golden-brown flecks
- Light or icy gray eyes. The iris has a silvery or steel blue tint with silver or white flecks
- Grey-blue eyes. The iris sports grey and blue elements
- Grey-hazel eyes. The iris features grey and hints of hazel
Genetic and Environmental Influences on Grey Eyes
Genetics plays a significant role in determining the color of a person’s eyes. Your parents' genes mingle and match to create endless possibilities, making your eye color a surprise until the day you're born.
Yes, even blue-eyed parents can have gray-eyed babies. It all boils down to a complex combination of inherited genes. But that doesn't mean it's the only factor involved.
Lighting and environment can also influence eye color to a lesser degree. For example, bright light can make grey eyes appear lighter, while dimmer environments can make them look darker.
And naturally, the color of a person’s eyes can change over time. Some people notice their eyes growing lighter or darker as they age. Sometimes, these changes can be temporary due to hormones, stress, or other environmental factors.
9 Facts About Grey Eyes
Here are nine interesting facts about grey eyes:
1. Grey-eyed People in Estonia
People often mix up blue and grey eyes, sometimes making statistics on them unclear. That said, Estonia, a Northern European country, may have the highest percentage of grey-eyed people. Almost 90% of the population has either blue or grey-blue eyes.7
2. More Likely to Drink
A study compared rates of alcohol dependence between those with light-colored eyes and those with dark eyes. It found a 54% higher rate of alcohol dependence among those with blue, green, light brown, or gray eyes.1
3. Changeable with Mood
Grey eyes "change" with the person's mood. This shift is due to how their pupils narrow or widen, which compresses or loosens the colors in the iris.
4. Linked to Wisdom
The Ancient Greeks associated grey eyes with wisdom. This association may have stemmed from the goddess of wisdom, Athena, who people often depicted with striking grey eyes.
5. Protection Against Disease
Emerging research suggests that gray-eyed people may have a natural defense against conditions like vitiligo.9 The skin disorder, linked to several serious health issues, including diabetes, arthritis, and lupus, may be less common among those with grey eyes.
6. Less Sensitive to Pain
A study found that pregnant women with brown or hazel eyes reported lesser pain tolerance than lighter-eyed women.5
7. More Sensitive to Sunlight
Due to their lack of melanin, people with grey eyes are more sensitive to sunlight, known as photophobia.10
8. More Competitive
A study in Current Psychology found that grey-eyed people are more likely to be competitive than those with dark eyes.3
9. More Strategic
A study from the University of Louisville has found that people's eye colors correlate with their performance in certain activities. Brown-eyed athletes excel in high-speed sports like football and hockey, while grey-eyed people thrive in sports that require more strategy and less reaction time. These included golf, cross-country running, and studying for exams.4
Eye Care Tips for Grey-Eyed People
Unlike brown eyes, grey eyes are more light-sensitive and may be more prone to dryness. Therefore, you must take extra care of them to keep them healthy.
Here are some tips to make sure your eyes stay healthy and beautiful:
- Wear sunglasses with UV protection to shield your eyes from the sun’s harsh rays
- Use a lubricating eye drop to keep your eyes hydrated and reduce the chances of irritation
- Clean your eyes gently with warm water and a soft cloth
- Visit your doctor for regular eye exams, especially if you experience any signs of vision changes
- Avoid putting too much pressure on your eyes by taking regular breaks from screens, books, and other activities that strain the eyes
With a hue so unique, grey eyes stand out from the crowd. So, confidently show off your beautiful gray eyes—and take good care of them.
Summary
- Grey eyes are rare and come in different variations.
- Different factors, such as genetics and lighting, can influence your eye color.
- Grey eyes are more light-sensitive than other eye colors, so extra care should be taken to keep them healthy.
- Proper eye care can reduce the chances of irritation and vision changes.
In this article
10 sources cited
Updated on September 24, 2024
Updated on September 24, 2024
About Our Contributors
Vincent Ayaga is a medical researcher and seasoned content writer with a bachelor's degree in Medical Microbiology. Specializing in disease investigation, prevention, and control, Vincent is dedicated to raising awareness about visual problems and the latest evidence-based solutions in ophthalmology. He strongly believes in the transformative power of ophthalmic education through research to inform and educate those seeking knowledge in eye health.
Dr. Melody Huang is an optometrist and freelance health writer with a passion for educating people about eye health. With her unique blend of clinical expertise and writing skills, Dr. Huang seeks to guide individuals towards healthier and happier lives. Her interests extend to Eastern medicine and integrative healthcare approaches. Outside of work, she enjoys exploring new skincare products, experimenting with food recipes, and spending time with her adopted cats.

