Updated on October 10, 2024
What to Know About Laser Iridotomy for Glaucoma


Vision Center is funded by our readers. We may earn commissions if you purchase something via one of our links.
What is Laser Iridotomy?
Laser peripheral iridotomy is a surgical procedure that restores the flow of aqueous humor for people with angle-closure glaucoma. Aqueous humor is the clear fluid in your eye that gives it shape and nutrients.
Angle-closure glaucoma occurs when there is a sudden blockage of the drainage angle located between the iris and cornea. It’s also called narrow-angle glaucoma.
When the drainage angle is blocked, eye fluid cannot flow at a normal rate. This increases intraocular pressure (IOP). An IOP elevation can permanently damage the optic nerve (communication pathway between the eye and brain). This can lead to vision loss and blindness.
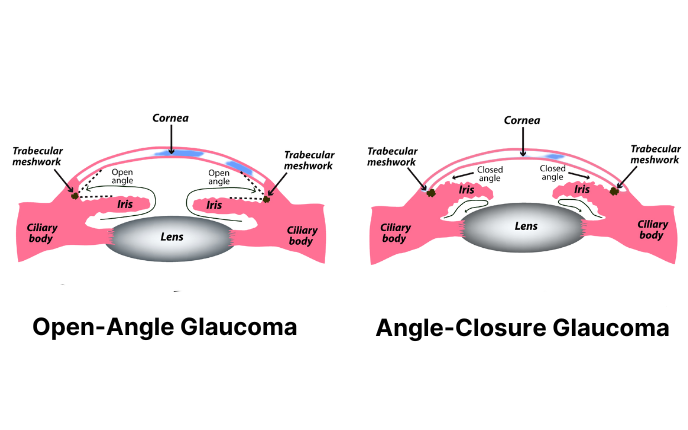
Symptoms of Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma
Symptoms of acute angle-closure glaucoma include:
- Blurred vision
- Headache
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Severe eyebrow pain
- Seeing halos or rainbows around light
Closed-angle glaucoma is a medical emergency. An ophthalmologist must treat it immediately before permanent vision loss or blindness occurs.
How Does Laser Iridotomy Work for Glaucoma?
The iridotomy procedure uses laser energy to create a small hole in the edge of the iris (colored part of the eye). This allows eye fluid to flow regularly while reducing intraocular pressure.
The procedure uses a yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) laser. While there is no cure for glaucoma, laser iridotomy is effective in:
- Lowering eye pressure
- Preventing further optic nerve damage
- Vision loss
- Blindness
Before the Procedure
Laser iridotomy is an outpatient surgery administered in an ophthalmologist's office or clinic. You can go home the same day as surgery.
Before the procedure, the eye doctor will check your intraocular pressure and administer eye drops to make your pupil smaller. They will also administer medicated eye drops to numb your eye.
To prepare for laser surgery:
- Eat a healthy breakfast
- Wear comfortable clothing
- Avoid wearing makeup
- Bring dark glasses for the drive home
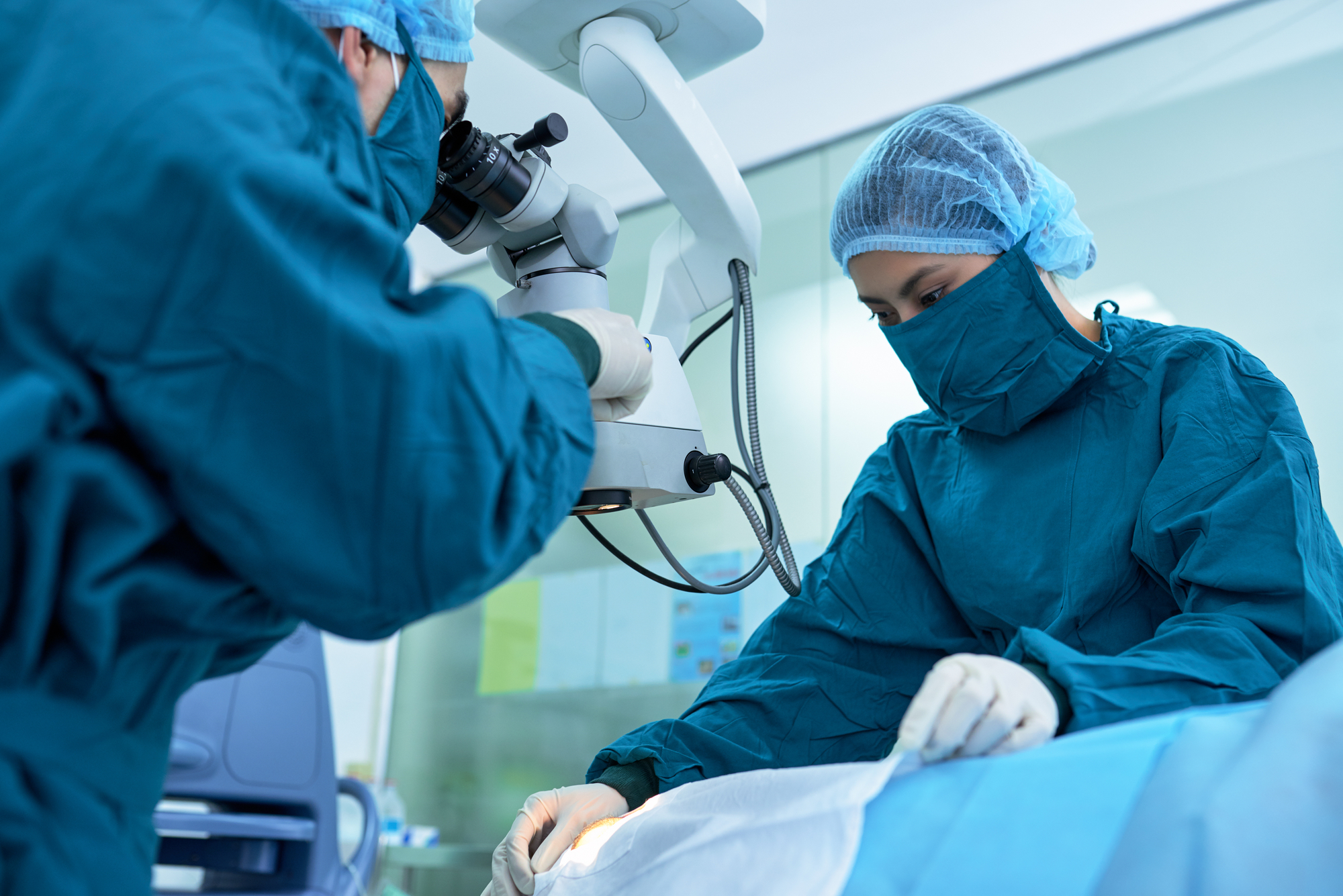
During the Procedure
During the procedure, you will sit in a comfortable position, and the doctor will:
- Place a special contact lens over your eye to guide the laser
- Use a slit lamp microscope to focus on the treatment area
- Create a small hole in the iris with the laser
Treatment typically feels like a pinprick sensation but is otherwise painless. You may hear a clicking sound and see a bright light similar to a photographer’s flash. The procedure takes about 5 to 10 minutes.
Aftercare & Recovery
About 30 minutes after the procedure, the eye doctor will recheck your intraocular pressure. After surgery, you:
- Will schedule a follow-up appointment for a week later to check the drainage angle
- Will administer anti-inflammatory eye drops daily for 4 to 7 days
- Have no restrictions on daily activities
- May experience blurry vision, which should clear the next day
- May experience mild discomfort and soreness for a few days
What is Eye Pressure?
Eye pressure, also called intraocular pressure, is maintained by the constant flow of aqueous humor through the drainage angle. Vision damage can occur if the flow rate is too low or too high.
Normal eye pressure is between 10 and 20 millimeters of mercury (mmHg). However, vision damage can still occur when IOP is within normal limits. This is called normal-tension glaucoma.
Glaucoma is when the optic nerve is damaged due to high IOP. Some people also have high IOP without vision loss or optic nerve damage, called ocular hypertension.
Who is a Candidate for Laser Iridotomy?
Laser iridotomy procedures are for those with anatomically narrow angles (primary angle-closure). People with anatomically narrow angles have a blocked internal drainage system within the eye.
The procedure can also be performed following an acute angle-closure attack, or as a preventative measure for narrow angles. Laser iridotomy is also recommended for people with:
- Acute angle-closure glaucoma (sudden spike in IOP)
- Chronic angle-closure glaucoma (when IOP increases over time)
- Secondary angle-closure glaucoma (increased IOP from another medical condition)
- Narrow drainage angle with normal eye pressure (used as a preventative treatment)
Who Shouldn’t Receive Laser Iridotomy?
Laser iridotomy has some contraindications. If you have any of the following conditions, treat them before getting laser iridotomy:
- Primary open-angle glaucoma
- Secondary glaucoma (increased eye pressure not caused by a closed drainage angle)
- Ocular media opacities (such as scarring or swelling of the cornea)
- Uveitis (eye inflammation)
- Problems tolerating laser eye surgery
Side Effects of Laser Iridotomy
Side effects of laser iridotomy are usually mild and include:
- Soreness
- Discomfort
- Redness
- Blurred vision
- Light sensitivity
- Headache
Side effects typically subside 24 to 72 hours after surgery.
What are the Risks?
Severe complications from laser iridotomy are rare, but as with any surgery, there are risks, including:
- Elevated eye pressure
- Bleeding at the treatment site
- Inflammation
- Visual disturbances (halos, rainbows, spots, shadows)
- Cataract development (cloudy area on the lens of the eye)
- Iridotomy closure (closing of the small hole created during surgery)
Laser iridotomy doesn't work for about 25% of people who undergo the procedure. In these cases, ophthalmologists and optometrists typically recommend medication and other forms of glaucoma surgery.4
Laser Iridotomy Outlook & Success Rates
Laser iridotomy has about a 60% success rate in:6
- Treating closed-angle glaucoma
- Reducing intraocular pressure
- Preventing further vision loss
The procedure effectively opens the drainage angle in about 75% of people. This makes it a safe and effective treatment for primary closed-angle glaucoma.7
Alternative Treatments
In addition to laser iridotomy, there are other ways to treat closed-angle glaucoma, including:
- Medicated glaucoma drops to reduce intraocular pressure
- Trabeculectomy to surgically create a small flap to open the drainage pathway
- Glaucoma drainage device, which surgically implants a tube to drain eye fluid
- Cyclophotocoagulation laser treatment that targets the “inflow” of eye fluid
- Cataract surgery, which removes the clear lens of the eye
Recent research has found that cataract surgery has been more clinically effective at lowering IOP for some people with narrow-angle glaucoma than laser peripheral iridotomy. This is a procedure that removes the eye’s lens.
Experts also found that cataract surgery to treat narrow-angle glaucoma resulted in:9
- Need for fewer glaucoma medications
- Less need for future glaucoma surgeries
- More cost-effective than laser iridotomy
Summary
Laser iridotomy is a surgical treatment for closed-angle and narrow-angle glaucoma. It uses a laser beam to create a small hole in the iris. This allows eye fluid to flow regularly and lower eye pressure.
The procedure is administered in an eye doctor's office or clinic, and you can go home the same day. Laser iridotomy takes 5 to 10 minutes and is usually painless.
Side effects are mild and include discomfort, soreness, redness, and temporary blurry vision. Closed-angle glaucoma is a medical emergency and could lead to permanent vision loss or blindness.
In this article
9 sources cited
Updated on October 10, 2024
Updated on October 10, 2024
About Our Contributors
Amy, a registered nurse with an M.S. in Nursing from California State University, Sacramento, and a B.A. in Journalism from California State University, Chico, is a freelance health writer for Vision Center. Her unique combination of nursing knowledge and journalism skills enables her to educate readers about eye health effectively. Amy's goal is to merge her nursing experience with her writing talent to raise awareness about common eye conditions and ways to prevent vision loss.
Dr. Melody Huang is an optometrist and freelance health writer with a passion for educating people about eye health. With her unique blend of clinical expertise and writing skills, Dr. Huang seeks to guide individuals towards healthier and happier lives. Her interests extend to Eastern medicine and integrative healthcare approaches. Outside of work, she enjoys exploring new skincare products, experimenting with food recipes, and spending time with her adopted cats.

