Updated on October 23, 2024
What Are the 3 Types of Eye Doctors?


Vision Center is funded by our readers. We may earn commissions if you purchase something via one of our links.
What are the 3 Types of Eye Doctors?
Three types of eye and vision care professionals provide different services. They include:
- Ophthalmologists
- Optometrists
- Opticians
All eye health professionals are focused on your vision. However, an ophthalmologist, optometrist, and optician all provide different services.
Some services may overlap, but these professionals have additional training and credentials.
Listen In Q&A Format
What Are The 3 Types Of Eye Doctors?
Vision Center Podcast
Ophthalmologist vs. Optometrist vs. Optician
Ophthalmologists, optometrists, and opticians all deal with eye health issues. However, beyond that, the care they provide is quite different.
An optometrist treats basic eye health issues. Ophthalmologists treat more advanced issues.
Opticians aren’t doctors. They don’t practice medicine, perform tests, diagnose diseases, or offer treatment aside from dispensing and fitting glasses and contact lenses.
Nevertheless, ophthalmologists, optometrists, and opticians work together to provide comprehensive eye care to people of all visual abilities.
1. Optometrists
An optometrist offers primary vision care. This is a doctor trained in the overall health of the eyes. They offer routine eye exams and a variety of different services.
Optometrists use a wide range of tests to check a patient’s vision. They also diagnose the presence of any diseases and offer treatment and maintenance of abnormalities.
When an eye disease has advanced beyond the optometrist's treatment capabilities, the patient is referred to an ophthalmologist.
The two often work together to help patients with pre and post-operative care, surgery, and recovery.
Education Level
Most Doctors of Optometry complete four years of undergraduate education and obtain a bachelor’s degree in pre-medical or biological sciences.
Doctors of Optometry need at least three years of post-secondary education focused on biology, chemistry, math, physics, and English.
Following their bachelor’s degree, optometrists must complete four years at a college of optometry to obtain their Doctor of Optometry degree.
What Conditions Do Optometrists Treat?
Optometrists are qualified to perform all basic vision tests and eye examinations. Many states allow optometrists to treat eye diseases like dry eye, glaucoma, and retinal diseases.
Some perform minor surgical procedures. They also provide pre and post-operative care.
Treatments Offered by Optometrists
Most people visit an optometrist for their annual comprehensive eye exam. Optometrists do the following:
- Provide and update contact lens and eyeglass prescriptions
- Prescribe medication and treatment for some eye conditions
- Diagnose eye conditions
- Perform minor surgical procedures, including LASIK and removal of foreign bodies (in some states)
- Provide pre and post-surgical care
Optometrist Equipment
Like all doctors, optometrists use a special collection of tools to care for patients.
This includes refractive aids that help them diagnose vision flaws and provide prescriptions for eyeglasses and contact lenses.
Optometrists also use a phoropter and eye chart to diagnose a person’s vision issues and write a corrective prescription.
When to See an Optometrist
You should see an optometrist at least once a year for an annual checkup and any time you experience eye health problems. Optometrists are the first line of defense when dealing with eye conditions.
They’re primary healthcare professionals, so they provide routine care and begin treating specific problems just like your family doctor or primary general practitioner.
Optometrists solve most vision health problems, but if they cannot, they’ll refer patients to an ophthalmologist.
Read More: How to Improve Your Eyesight
2. Ophthalmologists
An ophthalmologist is a medical doctor (MD) or a doctor of osteopathic medicine (DO).
Ophthalmologists have the most education of any eye health care provider. They diagnose eye diseases and treat them surgically when needed.
Optometrists refer most patients in need of eye surgery to an ophthalmologist. A referral is also likely for patients with more complicated or progressive eye diseases.
Education Level
Ophthalmologists complete at least three years of undergraduate education focusing on pre-med and/or science. They also receive an additional four years of medical training to become an MD or DO.
Medical school graduation is followed by a three-year residency studying eye diseases and surgical methods. Some ophthalmologists choose additional specialized training and develop a sub-specialty through a fellowship focused on a specific eye health condition.
What Conditions Do Ophthalmologists Treat?
Ophthalmologists treat advanced eye conditions. The most common issues they deal with include:
- Cataracts
- Glaucoma
- Eye infections
- Optic nerve problems
- Strabismus
- Ptosis
- Pterygium
- Persistent styes
Treatments Offered by Ophthalmologists
Some ophthalmologists provide basic eye care, while others also offer specialized treatment. This includes:
- Medical and surgical treatments
- Rehabilitation after surgery
- Medication for severe eye infections
- All types of eye surgery, including LASIK and cataract surgery
Ophthalmologist Equipment
Ophthalmologists are trained in using a variety of equipment, including:
Ophthalmoscope
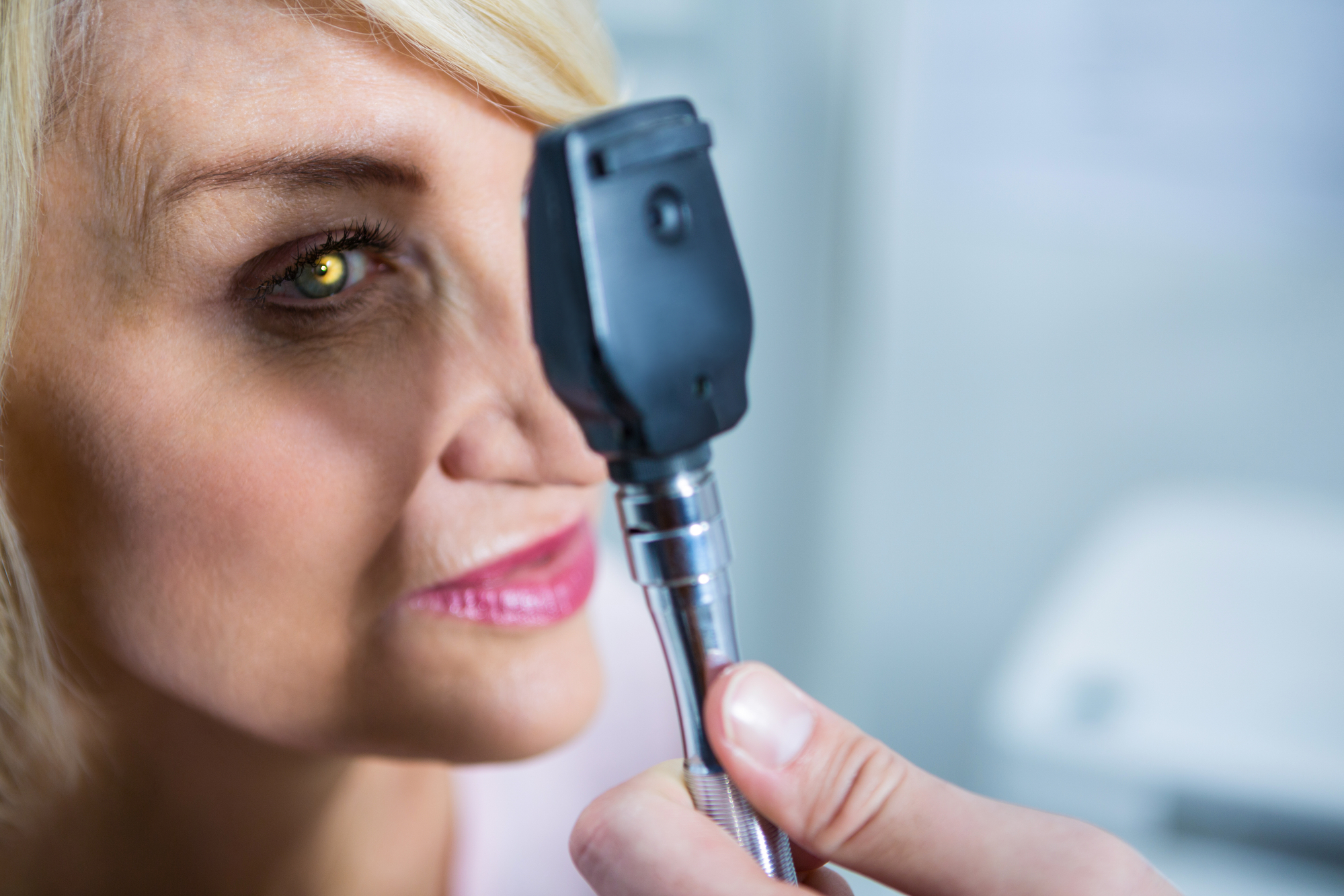
An ophthalmoscope is a hand-held device used to examine the eye’s interior.
It features a concave mirror that allows a doctor to look at the eye in various magnifications when used with a light source. It lets the doctor examine the cornea, lens, vitreous, and retina.
Retinoscope

A retinoscope is often used with young patients or patients with communication challenges.
It shines a beam of light directly into the retina. It lets the doctor observe the movement of the red reflex (reflection off the retina) and determine the lens power that provides a clearly defined image for the retina.
Phoropter
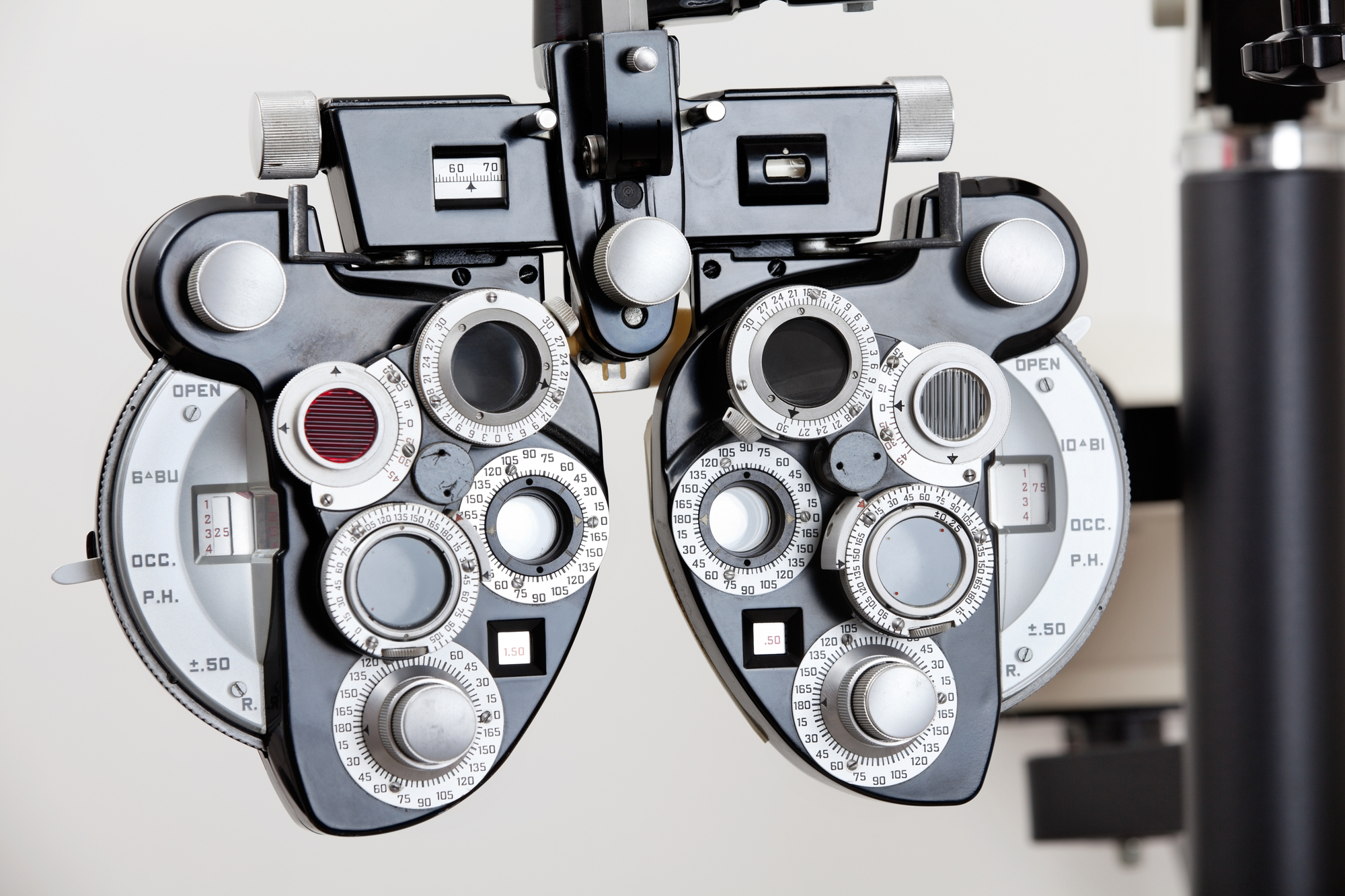
Doctors use a phoropter and an eye chart to assess a patient’s vision.
It has three rotating disks containing a variety of lenses and colored filters. Patients look at the chart through various lenses and describe their ability to view the eye chart.
Eye Chart

Doctors use an eye chart with a phoropter to assess a patient’s vision. He or she looks through the phoropter at the chart featuring several lines of letters.
The most common vision chart is the Snellen eye chart. It has multiple rows of random capitalized letters with one large top letter and progressively smaller letters.
The Tumbling E chart features only the letter E facing in different directions for patients who do not know the alphabet.
Additionally, ophthalmologists use surgical equipment, including the microkeratome device (used in LASIK procedures).
When to See an Ophthalmologist
There are several instances in which you would want to see an ophthalmologist. Most people begin with a visit to the optometrist, who then refers them to an ophthalmologist due to advanced eye health needs.
Some of these include:
- Cataracts. A progressive opacification of the lenses of the eyes; can cause vision impairment and require surgical removal
- Glaucoma. An eye disease characterized by damage to the optic nerve
- Age-related macular degeneration. A condition that can be diagnosed as dry or wet and affects the macula, responsible for detailed central vision
- Diabetic retinopathy. A degenerative complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness
- Strabismus. A condition that causes an eye turn and requires corrective lenses or surgery to treat
- Ptosis. This eye condition refers to weakened muscles that cause the eyelids to droop and block vision
- Pterygium. A condition that leads to fleshy growth on the front of the eye (over the conjunctiva) and may cause obstructed vision
- Persistent styes. Recurrent stye development that is uncomfortable and unsightly and requires professional excision
3. Opticians
Opticians work with eye doctors to ensure patients get the best eyewear based on their prescription. Many vision clinics have opticians on staff.
Opticians provide routine care, adjustment, eyeglasses, and contact lens refills. They aren’t doctors, but they can answer general eye care questions.
These professionals play an important role in advising and dispensing glasses and contacts. Here are some daily tasks of an optician:
- Receive and refill eyeglass and contact lens prescriptions
- Measure, fit, and adjust eyeglasses frames
- Help people choose frames, contacts, and other eyewear accessories
- Perform general operational duties at the vision care clinic or office
When to See an Optician
An optician can help you if:
- You are having difficulty seeing far away or up close based on your current glasses prescription
- You’re suffering from frequent headaches
- Your eyes are frequently dry or uncomfortable
- You’re squinting more than usual
- Medication has changed your vision
Tips: How to Choose The Right Eye Doctor
Choosing the right eye doctor can feel overwhelming. It helps to understand what each type of eye doctor does:
- Optometrists. They provide basic care and offer examinations, diagnoses, and medical treatment for eye conditions. They’re the first doctors to see when you have eye health issues or for your annual exam.
- Ophthalmologists. They specialize in surgical procedures for the eyes. They treat more advanced eye health issues.
- Opticians. They work in vision care centers and optometry offices and help patients get the necessary vision correction devices.
Choosing which of these eye health experts to visit should be based on your vision health and the services you need.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Eye Doctor
Once you know what kind of eye doctor fits your needs, your choice depends on a few factors. These include:
Insurance Coverage
You should also look for an eye doctor covered under your vision insurance. A doctor who is in your network can be substantially less expensive than a doctor who is not in your network.
Location
If you need to visit your eye doctor multiple times, consider the location of their practice. You should try to find eye health professionals near your area so you don’t have to travel far. This can make a huge difference in convenience.
Professionalism
Ensure you see an eye doctor who makes you feel heard and doesn’t invalidate your concerns. Your ocular health is critical, so you must find a doctor with whom you’re comfortable.
Summary
Choosing an eye doctor for your vision needs is an important decision. It’s best to understand what each eye health professional does and how they can help you.
You should also consider a few factors, such as insurance coverage, location, and professionalism. Once you’ve considered these, you can make an informed decision.
In this article
6 sources cited
Updated on October 23, 2024
Updated on October 23, 2024
About Our Contributors
Kelly Brown, a content writer for Vision Center, is dedicated to sharing vital information to assist individuals in making informed decisions about their vision health. Her writing covers a range of topics, from selecting the best eye doctor to addressing health issues impacting vision, with the aim of educating readers through informative and engaging content.
Dr. Melody Huang is an optometrist and freelance health writer with a passion for educating people about eye health. With her unique blend of clinical expertise and writing skills, Dr. Huang seeks to guide individuals towards healthier and happier lives. Her interests extend to Eastern medicine and integrative healthcare approaches. Outside of work, she enjoys exploring new skincare products, experimenting with food recipes, and spending time with her adopted cats.

