Updated on October 1, 2024
How Does an Astigmatism Test Work?


Vision Center is funded by our readers. We may earn commissions if you purchase something via one of our links.
If you have blurry or distorted vision at all distances, astigmatism may be the underlying problem.
An online astigmatism test can be a good starting point to identify a possible astigmatism. However, an at-home astigmatism test isn’t an accurate or precise way to diagnose astigmatism.
The only way to get an official diagnosis for astigmatism is to have your eyes checked by an eye care professional. This article explores what astigmatism is, its symptoms, and how to test for astigmatism.
How to Test for Astigmatism
The best way to determine if you have astigmatism is to schedule an evaluation with a medical professional, such as an optometrist or ophthalmologist.
Professional Eye Exam
Your eye doctor will perform a comprehensive eye exam to test for astigmatism. They’ll examine your overall eye health and visual acuity (visual sharpness).
You may be asked to cover one eye and read letters on an eye chart. You may also undergo other exams with several different devices.
How They Work
Your eye doctor may use the following tools during your eye exam:
- A phoropter. This device helps the eye doctor to determine the correction needed to improve your vision. You will look through different lenses so your eye doctor can see which is most suitable for your vision.
- An autorefractor. This device gives the eye doctor a starting point to refine your prescription. It shines light into the eye and measures how it changes when it returns from the back of the eye.
- A keratometer. This device helps measure the curve of your cornea. Your eye doctor may also include a corneal topography to learn more about the corneal surface and its shape.
Online Astigmatism Test
Another option to help determine if you have astigmatism is an online test. Multiple online tests are available and can serve as an initial means to identify a vision problem.
Remember that while online tests are helpful, they’re not conclusive. Online testing relies on your judgment and cannot effectively diagnose astigmatism. To get a confirmed diagnosis of astigmatism, you’ll need to follow up with an eye care professional.
How They Work
The tests are simple. You will look at a display of shapes and lines while standing a certain distance from the monitor. During this test, you will have to cover your left and right eyes, alternating between both.
What is Astigmatism?
Astigmatism is a common type of refractive error. A refractive error is when your eye cannot refract (bend) light properly onto the retina. Astigmatism affects about 36% of adults in the U.S.6
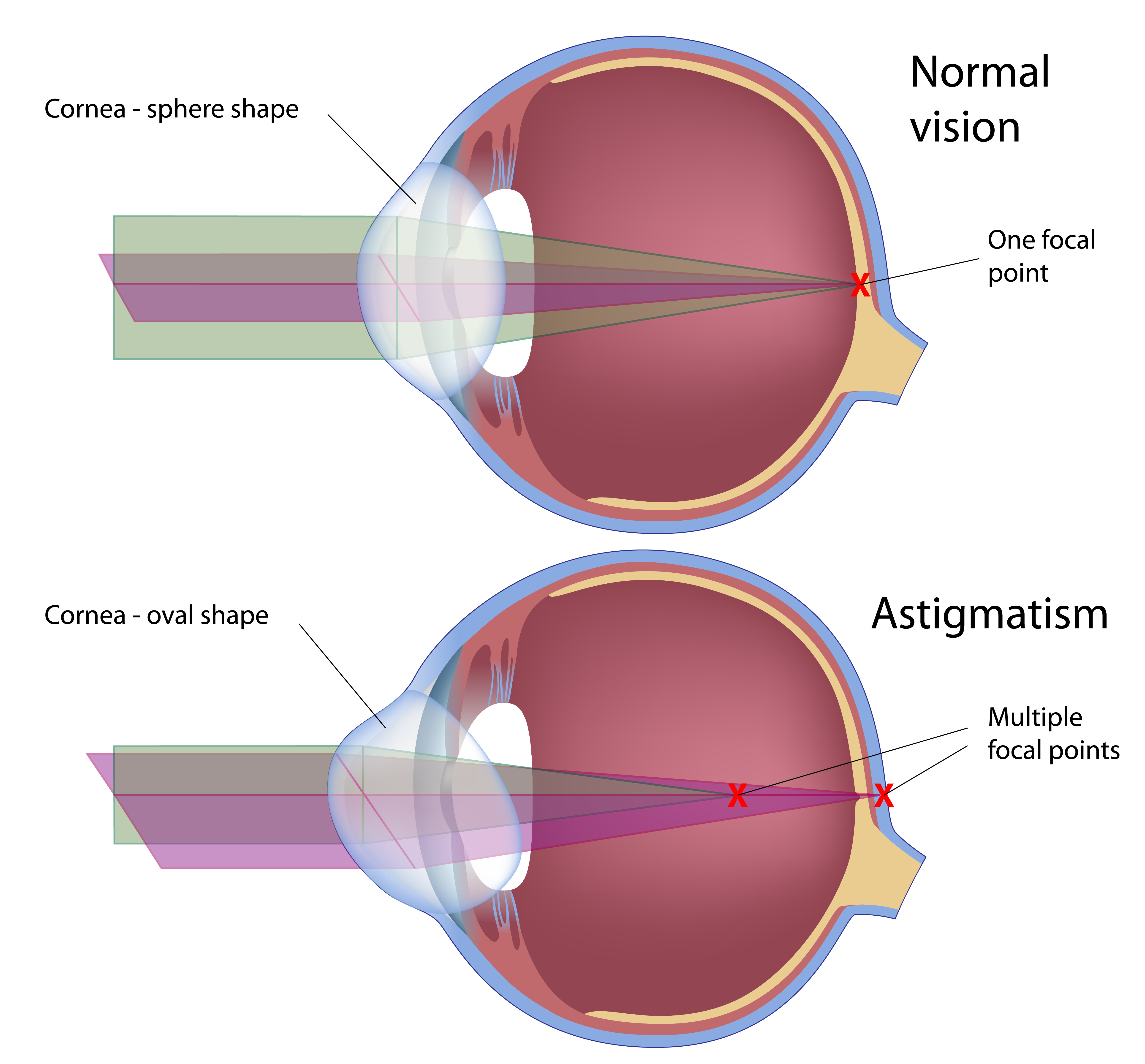
Astigmatism occurs when the curvature of the cornea or lens is irregular. The curvature may appear as a football or egg instead of a round ball. Because of this incorrect eye formation, you can find viewing objects difficult.
Many people with astigmatism have other refractive errors, such as myopia (nearsightedness) or hyperopia (farsightedness). All these conditions are treatable with corrective lenses or refractive eye surgery, such as LASIK.
What Are the Main Symptoms of Astigmatism?
Mild astigmatism may not cause noticeable symptoms. In more severe cases of astigmatism, you may have symptoms that include:
- Blurry vision
- Eye strain
- Headaches
- Dry eyes
- Squinting
- Eye discomfort
- Night glare
- Light sensitivity
Some people may confuse astigmatism with amblyopia (lazy eye). These eye conditions are not the same. However, severe astigmatism can contribute to amblyopia.
What Are the Levels of Astigmatism?
Ophthalmologists and optometrists measure astigmatisms in diopters. A perfect eye with no astigmatism will have 0 diopters. However, many people have between 0.5 to 0.75 diopters of astigmatism.5
With eye prescriptions, there are two areas or numbers that refer to astigmatism:
- Cylinder. Reflects how steep or irregular the curvature of your cornea is
- Axis. Shows where the astigmatism is on the cornea; ranges from 0 to 180 degrees
Treatment Options for Astigmatism
There are many ways to correct astigmatism. Treatment for astigmatism may include:
Astigmatism Glasses
Eyeglasses for people with astigmatism have a special cylindrical lens prescription. This means that specific parts of the lens boast additional power.
In many cases, a single-vision lens may work to provide clear vision at any distance. You may need bifocals or progressive lenses if you’re over 40 and have presbyopia.
Contact Lenses
Contact lenses that treat astigmatism are called toric lenses. There are many types of toric lenses available.
Depending on your needs, you may benefit from soft or rigid gas-permeable (hard) contact lenses. Your optometrist or ophthalmologist will help you determine the best lens type for your eyes.
Eye Surgery
Laser refractive surgery, such as LASIK, can treat astigmatism and reduce the need for eyeglasses and contact lenses. LASIK stands for laser in situ keratomileusis. It involves reshaping the cornea with a laser.
However, not everyone is a good candidate for LASIK. If LASIK isn’t right for you, your eye specialist may recommend PRK or LASEK.
Summary
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error that results from irregular curvature of the eye. It can cause night glare and blurred vision at all distances.
An online astigmatism test can provide an idea of whether you have astigmatism. However, seeing an eye specialist for an accurate diagnosis and treatment is necessary.
In this article
6 sources cited
Updated on October 1, 2024
Updated on October 1, 2024
About Our Contributors
Anthony Armenta, a graduate in International Relations from the University of California, Irvine, has dedicated the past 5 years to freelance health content writing and medical editing in Barcelona. Working with public hospitals, he covers various medical specialties, including infectious diseases and pneumology. Anthony's commitment to creating fact-driven, health-related content is driven by his belief in the power of information to empower individuals to improve their health, including in areas like vision care.
Dr. Melody Huang is an optometrist and freelance health writer with a passion for educating people about eye health. With her unique blend of clinical expertise and writing skills, Dr. Huang seeks to guide individuals towards healthier and happier lives. Her interests extend to Eastern medicine and integrative healthcare approaches. Outside of work, she enjoys exploring new skincare products, experimenting with food recipes, and spending time with her adopted cats.

